Newborn screening is a public health intervention done within 72 hours of birth. It involves three major tests to identify life-threatening genetic illnesses, even before the symptoms kick in.
Statistically, it can be claimed that most of the newborn babies are healthy and won’t have any of the conditions the screening tests are looking for. But, for the babies who do have problems, the benefits offered by the screening can be enormous. Early treatment and proper guidance from the Physician can prevent severe disabilities, sometimes even death.
From 1996-2015, it is revealed that G6PD Deficiency and Congenital Hypothyroidism were found as the two most identified major issues.
Heel Prick Test
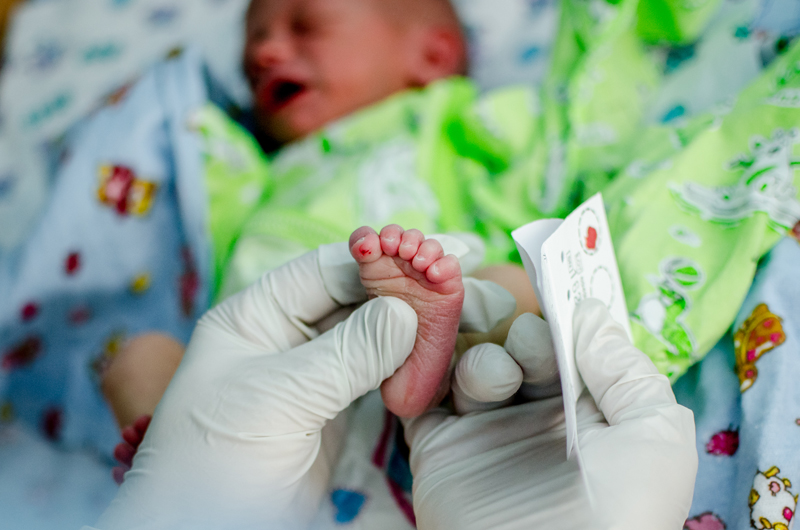
Similar to a blood test, every baby should be subjected to newborn blood spot screening, which is known as the heel prick test. During this test, the baby’s heel will be pricked to collect a few drops of blood. Usually, the parents are allowed to be present during this test and they can minimize any distress to the baby by cuddling and feeding. The blood is sent to a lab for analysis. Consider this as mandatory if there is a family history of certain conditions or other health concerns. This blood spot test screens for more than 50 possible serious conditions and ensures a better future for the little one.
If the test confirms the possibility of getting a serious issue, additional tests will be preferred to reconfirm the same. Even if the test is positive, there is nothing to worry, as the preventive treatment will ensure there won’t be any serious problems in the future.
Hearing Test
Various studies indicate that one to two babies in every 1000 are born with permanent hearing loss either in one or both ears. The newborn hearing screening test helps to identify conditions such as hearing loss as early as possible. This will help the parents to get the right support from the start.
Two different tests are usually offered during this process.
Automated Otoacoustic Emission (AOAE) test: A small soft-headed ear piece will be placed in the baby’s ear and gentle clicking sounds are played. If the baby’s hearing condition is normal, an echo is reflected back into the ear canal. If no echo is detected, it indicates there is hearing loss.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) test: During this test, three small sensors are placed on the baby’s head and neck. Soft headphones are placed over its ears and again gentle clicking sounds are played. This is used to evaluate the auditory brain stem and the brain’s response to sound.
This is a non-invasive test to measure the levels of oxygen in the baby’s blood. Infants with heart problems may have low oxygen levels in the blood. With this, babies with Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) can be identified. This will help the parents to take necessary precautions so that the effect of the condition can be reduced in the future.
Apart from these three primary tests, all the hospitals mandatorily offer a thorough physical examination.
General Physical Examination
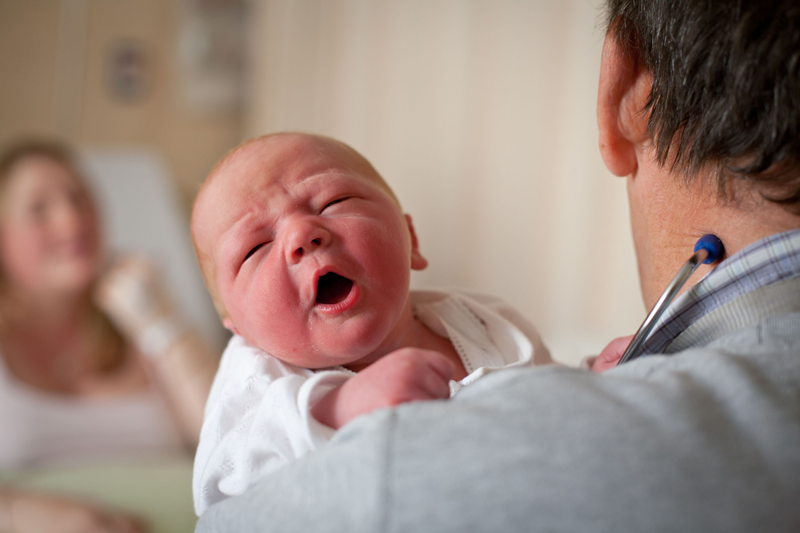

This examination includes specific screening tests to find problems in the eyes, heart, hips and, in boys, the testicles (testes).
The aim of the test is to spot any problems so that early treatment can be deployed. If the examiners find a possible problem, they may refer your baby for more tests. Usually, a second physical examination may happen at six to eight weeks, to confirm or dismiss the conditions detected earlier.
What are the tests?
- Examining baby’s eyes with a special torch called Ophthalmoscope and check how they respond to light
- Listening to the baby’s heart to check their heart sounds and heart beat rate
- Examining the physical structure, mainly the hips to check the joints
- For baby boys, examination of their testicles may also be carried out
On the other hand, it is important to know that screening is not 100% certain all the time. False negatives and false positives often occur in all the tests and the Newborn Screening tests are no different. But it can be the pointer to find out the issues in advance so that you can prepare for minimizing the effects in the future.

